5'Nucleotides and Nucleic Acid Analysis in Yeast Extracts

Yeast extract serves as a highly nutritious and flavorful ingredient in food and feed formulations. Derived from carefully processed yeast cells, it's packed with essential nutrients that make it a valuable addition to various products.
Key Nutritional Components:
- High-quality proteins with complete amino acid profile
- Essential B vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, B12)
- Minerals including zinc, selenium, and potassium
- Nucleotides and nucleic acids (6-12% of dry weight)
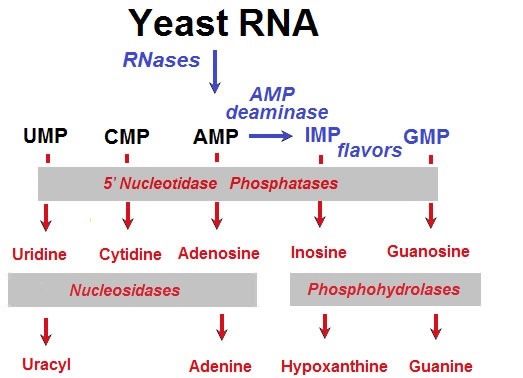
Figure: Conversion of yeast RNA into flavor-enhancing nucleotides
Nucleotide Production Process
Yeast RNA undergoes enzymatic hydrolysis to produce four primary 5'-nucleotides:
- 5'AMP (Adenosine Monophosphate)
- 5'GMP (Guanosine Monophosphate)
- 5'UMP (Uridine Monophosphate)
- 5'CMP (Cytidine Monophosphate)
Flavor Enhancement
For optimal umami taste, 5'AMP is converted to 5'IMP using AMP-deaminase, creating a more balanced and savory flavor profile in yeast extracts.
Our Service of Yeast Extract Nucleotide Analysis
| REFERENCE | SERVICE DETAILS | PRICE | ACTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| #S1200-03 |
Comprehensive Yeast Extract AnalysisOur HPLC-UV analysis provides a complete profile of nucleotide content in yeast extracts, including:
|
€420.00
per sample
|
Request Analysis |
Detailed description
- Step 1: Sample solubilization and proteolytic hydrolysis
- Step 2: Standards preparation for calibration of ion-paired UV-HPLC. Molar concentration of each of 20 standards is confirmed by measuring their absorbance at 249–254 nm.
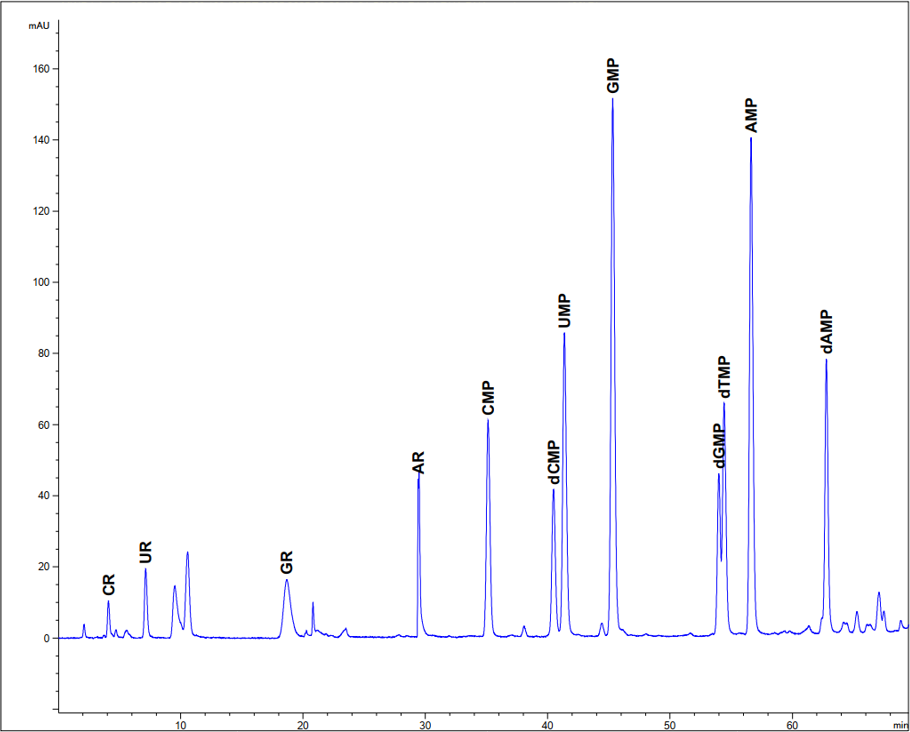
- Step 3: Enzymatic hydrolysis of nucleic acids with nucleases to hydrolyze all nucleic acids into 5′NMP and 5′dNMP.
- Step 4: Determination of soluble bases, nucleosides and nucleotides before and after RNA and DNA hydrolysis by ion-paired HPLC-UV with simultaneous separation of apolar bases, nucleosides, polar NMP and dNMP in one run.
- Step 5: As our internal Quality Control, we measure 5'IMP and 5'AMP concentration using independent enzymatic PRECICE® Nucleotide Assay Kit and compare the results of enzymatic assay and HPLC analysis.

 PRECICE® Enzymatic assay
PRECICE® Enzymatic assay
 PRECICE® Enzymatic assay
PRECICE® Enzymatic assay
Data produced are used to calculate the content of each individual bases, nucleosides and NMP (g/kg or g/100g) or purines content (bases adenine, guanine, xanthine and hypoxanthine)
| Name | Chemical Class | g / 100g |
|---|---|---|
| Cytosine | 0.00 | |
| Uracil | Bases, pyrimidine | 0.07 |
| Guanine | Bases, purine | 0.00 |
| Hypoxanthine | Bases, purine | 0.21 |
| Adenine | Bases, purine | 0.21 |
| Cytidine | Nucleoside, pyrimidine | 0.12 |
| Uridine | Nucleoside, pyrimidine | 0.23 |
| Guanosine | Nucleoside, purine | 0.63 |
| Inosine | Nucleoside, purine | 0.04 |
| Adenosine | Nucleoside, purine | 0.54 |
| Na₂*CMP | Nucleotide monophosphate, pyrimidine | 4.21 |
| Na₂*UMP | Nucleotide monophosphate, pyrimidine | 3.06 |
| Na₂*GMP | Nucleotide monophosphate, purine | 4.17 |
| Na₂*IMP | Nucleotide monophosphate, purine | 0.00 |
| Na₂*AMP | Nucleotide monophosphate, purine | 4.19 |
| Total NMP | Soluble Nucleotide Monophosphates | 15.63 |
| Nucleic acids (RNA) | Nucleotides monophosphate Released after nuclease digestion | 2.83 |
| Total NMP | 15.63 | |
| Total potentially available nucleotides (TPAN) | 20.53 | |
Technical Challenges in Yeast Extract Production
Maintaining optimal 5'-nucleotide levels requires careful control of several critical factors throughout the production process.
Enzyme Activity Management
Critical Issue
Uncontrolled enzyme activity can significantly reduce the quality of flavor-enhancing nucleotides.
Key Challenges:
-
Phosphatases: Remove phosphate groups from nucleotides
Result: Loss of 5'-nucleotide flavor enhancers
-
5'-Nucleases: Break down RNA into non-flavor active components
Result: Reduced yield of desirable nucleotides
RNA Hydrolysis Optimization
Technical Insight
Efficient RNA breakdown is crucial for maximum 5'-nucleotide yield.
Common Issues:
-
Incomplete Hydrolysis: Leaves RNA partially broken down
Result: Lower yields of target nucleotides
-
Protein-RNA Complexes: Protect RNA from enzymatic action
Result: Inconsistent nucleotide profiles
Understanding RNA Co-Purification in Yeast Proteins
The RNA Challenge in Yeast Protein Products
Yeast proteins have emerged as a sustainable, high-quality alternative to traditional animal proteins, offering complete amino acid profiles and excellent nutritional value. However, the production process often results in significant RNA co-purification, especially when using microfiltration techniques.
Important Health Consideration
Excessive dietary RNA can lead to elevated uric acid levels. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) recommends a maximum daily intake of 2 grams of RNA for adults to prevent potential health issues.
Why Choose Our Analysis Services?
With years of experience in nucleotide analysis, we provide accurate, reliable results with fast turnaround times and comprehensive reporting to help you optimize your yeast-based products.
- Complete Profile: Analysis of all nucleotide species
- Precision: Accurate quantification of RNA/DNA content
- Compliance: Ensure regulatory requirements are met
- Quality Control: Monitor production consistency
